Describe the Anatomy of the Breast
The breast is the tissue overlying the chest pectoral muscles. The main chest muscle the pectoralis muscle is found between the breast and the ribs in the chest wall.
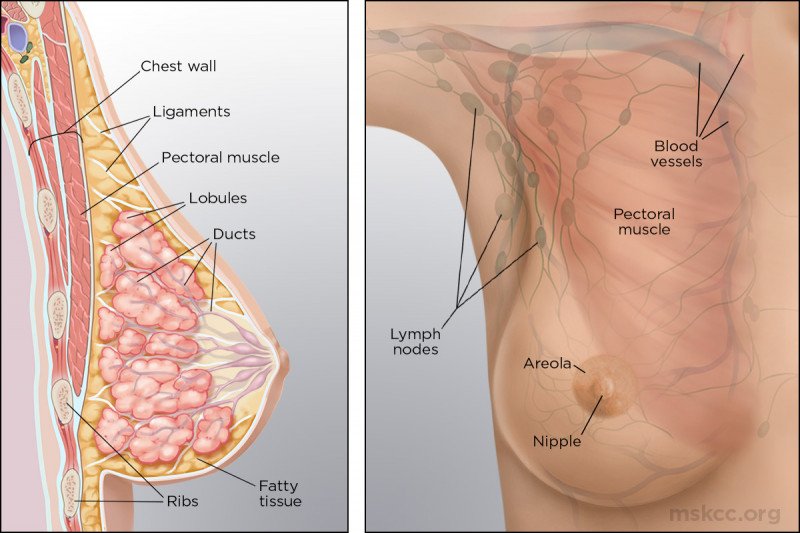
Anatomy Of The Breast Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Describe the anatomy of the breast.

. In women the breasts are composed principally of specialised tissue glandular tissue that produces milk. These are the so-called milk ridges or milk lines. Aspects of the thorax.
Lactation is the process by which milk is synthesized and secreted from the mammary glands of the postpartum female breast in response to an infant sucking at the nipple. The lobes lobules and bulbs are all linked by thin tubes called ducts. Tiny openings in the nipple allow milk to flow.
The Anatomy and Physiology of the Breast. The structure of the breast. The nature of the superficial fascia system that surrounds the breast and its attachments to the chest were studied in 12 cadaver breast dissections and in clinical cases of both cosmetic and reconstructive breast.
Within these tissues are milk-producing cells. Figure 11 shows the different parts of the breast. Development of the Human Breast.
Surrounding the nipple is the areola an area of darker skin that becomes both larger and darker during pregnancy. Fibrous or supportive or connective tissue is the same tissue that ligaments and scar tissue are made of. Breasts are made up of fat and breast tissue along with nerves veins arteries and connective tissue that helps hold everything in place.
New imaging techniques show. It is quite common to have breast tissue up toward and even in the armpit. Glandular tissue includes the breast lobes and breast ducts.
Within each lobe are many smaller lobules which end in dozens of tiny bulbs that can produce milk. Each breast consists of tissue overlying the chest wall muscles the pectoral muscles. The epithelial component of the tissue consists of lobules where milk is made which connect to ducts that lead out to the nipple.
Fewer milk ducts average 9. The breast is a modified sweat gland located in the superficial fascia of the anterior chest wallThe major portion of the breast tissue is situated between the second and third rib superiorly the sixth and seventh costal cartilage inferiorly the anterior axillary line laterally and the sternal border medially. The parenchyma forms a system of branching ducts eventually leading to secretory acini development and the stroma consists mainly of adipose tissue providing the environment for development of the parenchyma.
Doctors refer to all non-fatty tissue as fibroglandular tissue. Breast milk provides ideal nutrition and passive immunity for the infant encourages mild uterine contractions to return the uterus to its pre-pregnancy size ie involution and induces a substantial metabolic. Each breast extends superiorly to the.
The amount of fat. It extends horizontally from the lateral border of the sternum to the mid-axillary lineVertically it spans between the 2nd and 6th costal cartilagesIt lies superficially to the pectoralis major and serratus anterior muscles. It grows along two ridges one on either side running from the armpit axilla to the groin.
1 2 3 These building blocks of the breast are recognized. The human breast consists of parenchymal and stromal elements. The authors set out to discover and describe a theory of superficial fascia structures responsible for breast shape.
Lactation is the process by which milk is synthesized and secreted from the mammary glands of the postpartum female breast in response to an infant sucking at the nipple. Anatomy of the breast Normal anatomy. Range 4-18 Milk ducts branch closer to nipple 65 of glandular tissue within 30mm radius from base Milk ducts are small and do not display lactiferous sinuses dilated portion beneath nipple-only dilate with milk ejection reflex.
Located between the second and 6th rib. Areola surrounds nipple with sebaceous glands montgomery glands- secretes protective lipid material Glandular Tissue Fibrous Tissue suspensory ligaments Adipose tissue. The remaining part is made up of fatty tissue.
Breast tissue begins to originate by the fourth week of fetal life. Fatty tissue fills in the spaces between glandular and fibrous tissue and largely determines your breast size. Be aware of anything unusual.
The production of milk for lactation breast feeding. The medical name for breast is mammary gland. Anatomy of the breast.
The breasts comprise glandular connective and fatty tissue. As you learn about breast cancer we will repeatedly reference the anatomy of the breast. 1 Cooper wrote concerning the fascia mammae that it contained two layers one anterior to the breast gland and one posterior to it.
The breast is located on the anterior thoracic wall. In humans breast tissue begins to enlarge at puberty. Have a better dialogue with your doctor.
Basic Facts About Breast Health. In 1840 Sir Astley Cooper published his book On the Anatomy of the Breast. The breast is an organ whose structure reflects its special function.
Knowing your body helps you to. The breasts are located on the a nterior and also partly the lateral. Tail of Spence in the axillary.
Breast tissue can develop anywhere along the milk line. The nipple anatomy is adjusted to support the function of the breastThey are surrounded by a pigmented circular region of skin called the areola which becomes even more pigmented and prominent during pubertyThe areola shows small punctual elevations on its surface which are produced by the many areolar glands. He described ligamenta suspensoria which connected to the skin and muscle.
Womens breasts are made of specialized tissue that produces milk glandular tissue as well as fatty tissue. Breast milk provides ideal nutrition and passive immunity for the infant encourages mild uterine contractions to return the uterus to its pre-pregnancy size ie involution and induces a substantial metabolic. There are literally thousands of drawings of the breast its blood supply lymphatic drainage and regional nerves that can be found in anatomy books and textbooks on breast disease.
Each breast has six to nine overlapping sections called lobes. Anatomy Physiology of the Breast. Understanding the different parts and functions will help you better grasp the details of breast cancer.
The breast is composed of 15 to 20 lobes in most women.
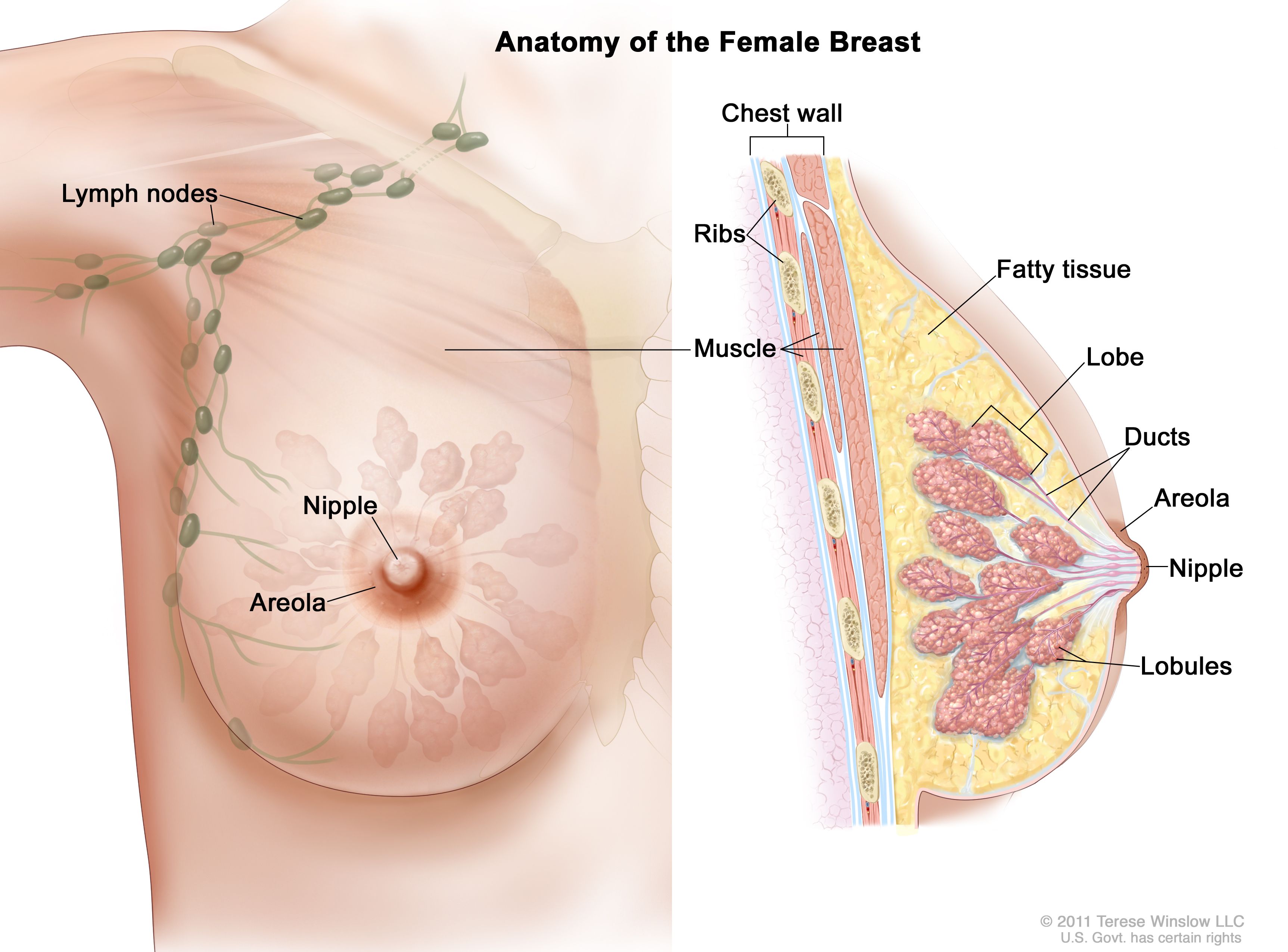
Definition Of Breast Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms National Cancer Institute

Breast Anatomy Breast360 Org The American Society Of Breast Surgeons Foundation
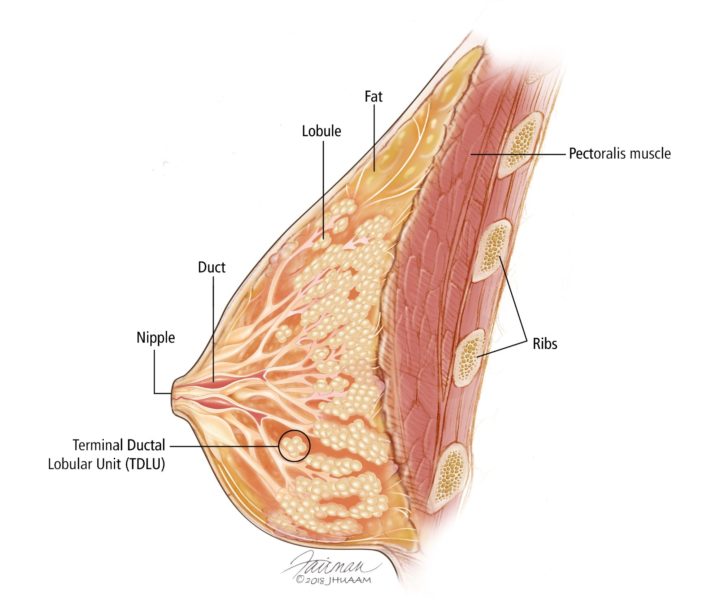
Overview Of The Breast Breast Pathology Johns Hopkins Pathology
Comments
Post a Comment